If you want to pinpoint your location in space, start with your cosmic address. You live in Earth → Solar System → Milky Way Galaxy → Local Cluster → Virgo Galaxy Cluster → Virgo Supercluster → Laniakea.
Thanks to new deep-sky surveys, astronomers now believe all these locations are part of a larger cosmic structure in the “neighborhood” called the Shapley concentration.
Astronomers refer to the Shapley concentration as the “basin of gravity.” It is a mass-loaded region that acts as an attractor. It is a region containing many galaxy clusters and groups, and is the region with the highest concentration of matter in the local universe. All these galaxies and dark matter exert their gravitational influence on the concentration.
There are many of these basins in space, including Laniakea. Astronomers are working to study them more precisely, which should help provide a more accurate map of the universe’s largest structures.
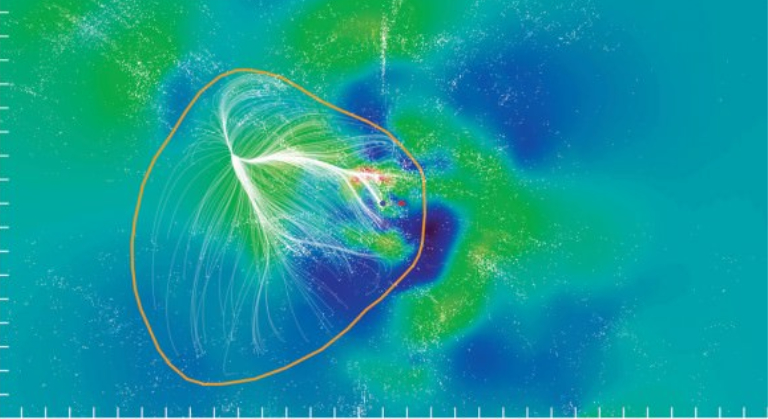
A group led by University of Hawaii astronomer R. Brent Talley measured the movements of about 56,000 galaxies to understand these basins and their distribution in the universe.
“Our universe is like a giant spider’s web, with galaxies lying along filaments and clustered into nodes that are pulled together by gravity,” Tully said.
“Galaxies flow within basins of cosmic gravity, just as water flows within basins. The discovery of these larger basins could fundamentally change our understanding of the structure of the universe.” there is.”
Cosmic flow and mapping structure
Talese’s team is called CosmicFlows, and it studies the cosmic motions of distant galaxies. The team’s redshift survey reveals that the size and scale of our local galaxy’s gravitational basin can change.
We already know that we live on Laniakea, which is about 500 million light years across. However, the movement of other clusters indicates that there are larger attractors directing cluster flow.
CosmicFlows data suggests we may be part of the Shapley Concentration Zone, which could be 10 times the volume of Laniakea. It is about half the volume of the largest structure in the universe, known as the Great Wall of Chinaa line of galaxies spanning 1.4 billion light years.
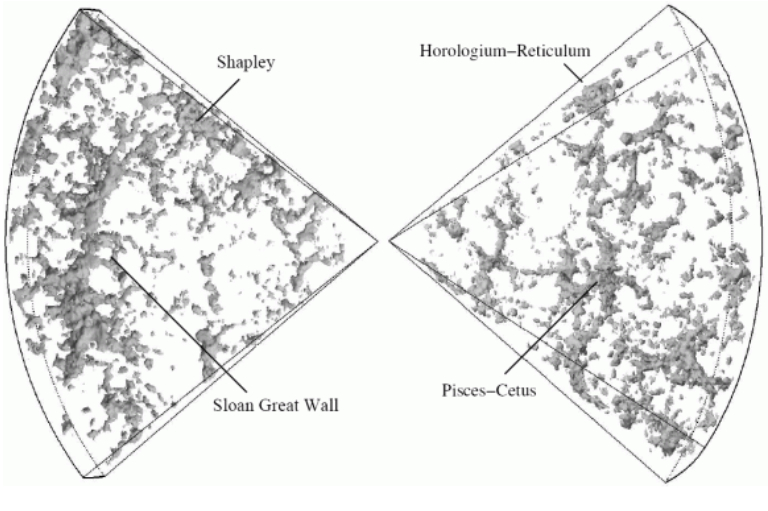
The Shapley concentration was first observed in the 1930s by astronomer Harlow Shapley as a cloud in the constellation Centauri. This supercluster appears along the direction of motion of the local group of galaxies (in which we live). Scientists therefore speculated that it might be influencing the unique motion of our galaxy.
Interestingly, the Virgo Supercluster (as well as the Local Cluster and the Milky Way) appears to be moving towards the Shapley concentration. The research Talley and his colleagues are conducting should support their movement towards what attracts them.
Exploring the ever-growing structures of the universe
Where do these basins of attraction come from? In a sense, they are as old as the universe and its web of matter that Tully refers to. The seeds of the webs and their basin of attraction were planted about 13.8 billion years ago.
After the Big Bang, the newborn universe was in a high-temperature, high-density state. As it expanded and cooled, the density of the material began to fluctuate. There were slight differences in these density fluctuations. Think of them as the earliest “seeds” of galaxies, galaxy clusters, and even more vast structures seen in the universe today.
When astronomers study the sky, they find evidence of various structures. Now they have to explain it. The idea that the Shapley Concentration is the large basin to which our Laniakea belongs means that current cosmological models do not fully explain its existence.
“This discovery presents a challenge: Our space surveys may not yet be large enough to map the full extent of these giant basins,” said the University of Washington astronomer. Ethan Krkuch said.
“We’re still looking through giant eyes, but even those eyes may not be big enough to capture the entire universe.”
Attractor measurement
Gravity is the dominant force in all these galaxies, galaxy clusters, and superclusters. The greater the mass, the greater the effect of gravity on the motion and distribution of matter.
For these gravitational basins, Talese’s research team investigated their influence on the movement of galaxies in the region. The basins act like a kind of tug-of-war on the galaxies between them. It affects their movement. In particular, redshift surveys like the one Tully’s team is conducting map radial motion (along the line of sight), velocity (how fast you’re moving), and other related motions. Masu.
By mapping the velocities of galaxies across our local universe, the research team is able to define the regions of space dominated by each supercluster.
Of course, these movements are difficult to define. Therefore, the team is conducting different types of measurements. They aren’t just mapping luminescent matter in galaxies. We also need to consider the presumed existence of dark matter.
There are other complications as well. For example, not all galaxies are the same. That is, they differ in shape (morphology) and material density. Astronomers can get around this by measuring something called the “galactic intrinsic velocity.” This is the difference between the actual velocity and the expected Hubble flow velocity (which reflects gravitational interactions between galaxies).
The Tally team’s findings should provide more accurate 3D maps of these spatial regions. This includes not only structure but also movement and speed. These maps should give deeper insight into the distribution of all matter (including cold dark matter) throughout the universe.
This article originally appeared on Universe Today. Read the original article.