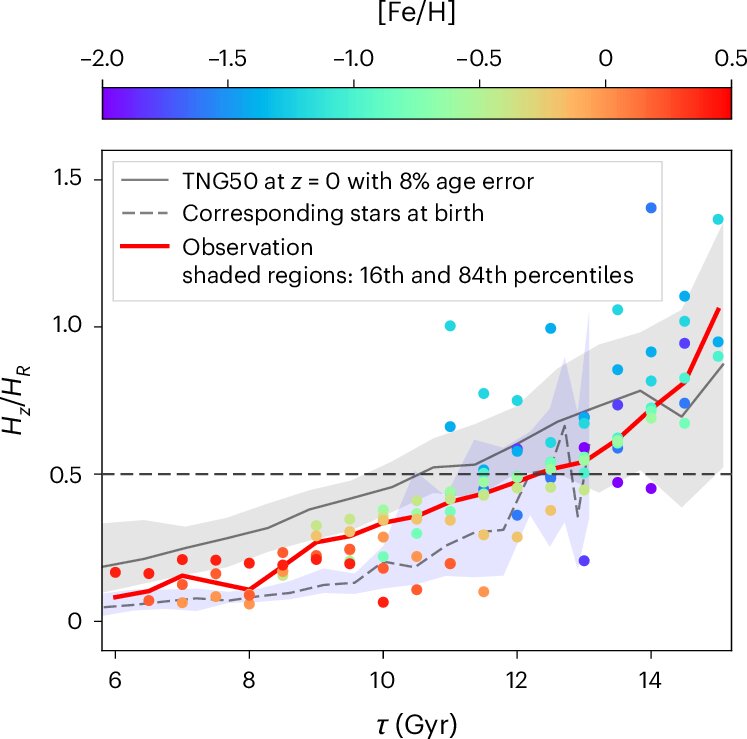
Compare Milky Way observations and TNG50 simulations and scale height to height ratio as a function of age. credit: natural astronomy (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41550-024-02382-w
A team of astronomers and astrophysicists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the University of Toronto has discovered what may be the oldest stellar disk in the Milky Way. Their study was reported in the journal natural astronomythis group used high-alpha stars with significant orbital angular momentum to perform age determinations of a wide range of stars in the galaxy.
Previous studies have shown that the Milky Way galaxy began as a single entity. Over time, it became much larger, drawing in multiple other galaxies. Such galactic remnants have been found throughout the Milky Way. Such additions have made it difficult for astronomers to determine the original structure of the Milky Way.
In this new effort, the researchers claim that by dating large numbers of stars in different parts of the galaxy, they were able to zero in on a specific group that they believe represents the original galactic disk. are. The team named the disc PanGu.
By dating the stars in the galaxy, researchers also found evidence that their combined mass is about 3.7 billion times that of the Sun. These discoveries cast doubt on traditional theories, as the first stars likely existed about 400 billion years after the Big Bang, or 13.4 billion years ago. Until about 12.5 billion years ago, it could not belong to a structural galaxy.
This suggests that the Milky Way has not had time to gain such mass. But the researchers were stubborn: Had star formation occurred at a constant rate, they could have achieved the mass they calculated, and the remaining stars in the early Milky Way would have died out as supernovae. It further suggests that there will be.
According to the research team, there are 2.2 billion solar masses left in the current disk, equivalent to just 0.2% of the current mass of the galaxy, and how much of the Milky Way is made up of material from other galaxies. It shows whether it is configured.
The researchers also suggest that there is evidence that the Milky Way reached its maximum size about 11 billion years ago.
Detailed information:
Maosheng Xiang et al., Formation and survival of the oldest stellar disk in the Milky Way, natural astronomy (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41550-024-02382-w
© 2024 Science X Network
quotation: Researchers retrieved the oldest stellar disk in the Milky Way galaxy from https://phys.org/news/2024-10-oldest-stellar-disk-milky-galaxy on October 16, 2024 ( October 15, 2024). html
This document is subject to copyright. No part may be reproduced without written permission, except in fair dealing for personal study or research purposes. Content is provided for informational purposes only.